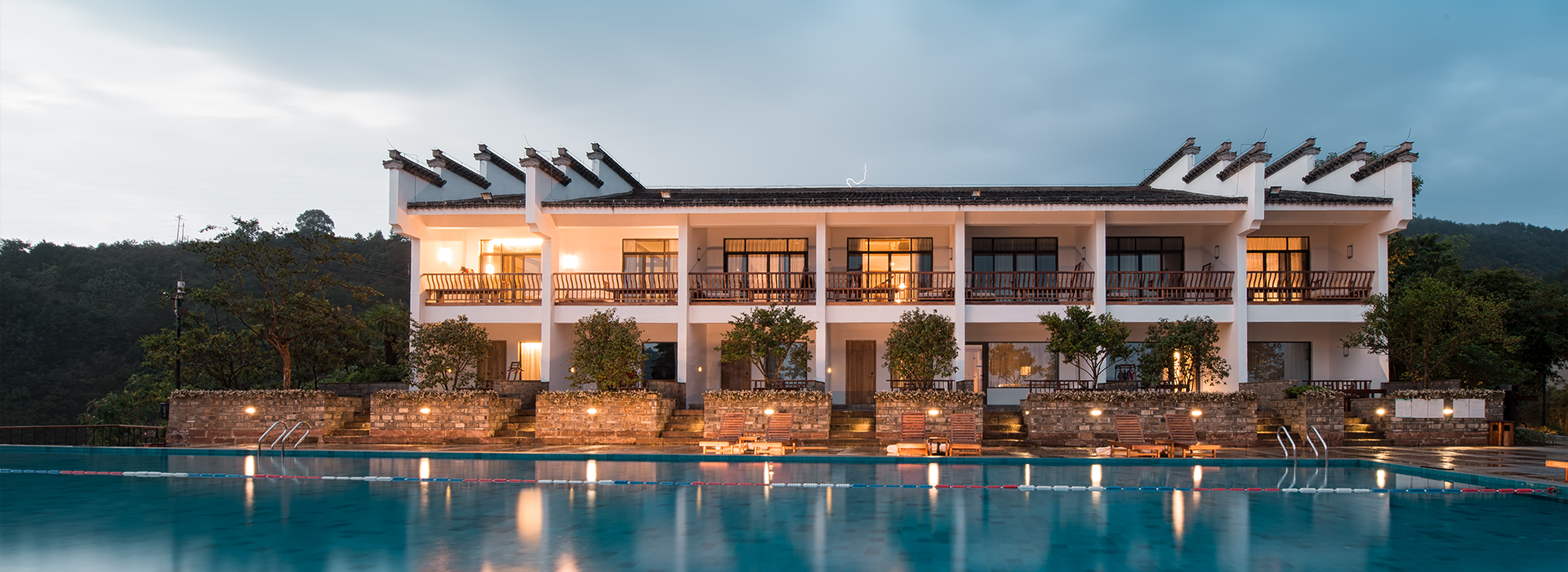
装配式建筑和模块化建筑的环境可持续效益
材料的再利用和回收
模块化结构的一个重要部分发生在异地工厂。该工厂通常存放项目材料和模块中经常使用的其他材料。如果订购了材料,但由于任何原因(如所有者改变主意、规格更改或其他原因)未使用,则材料不会被浪费或丢弃。相反,这些材料被回收再利用。未使用的材料可以重新盘点并储存在工厂的仓库中,以备将来用于其他项目。反过来,木质托盘、塑料和纸板等材料包装也在减少。因此,材料的可重用性减少了项目产生的废物总量。
物料室外管控
由于项目的许多材料存储在异地工厂中,这些材料在停工期间不会受到室外条件的影响。它们通常储存在仓库内,在那里,它们可以避雨,雪,高温,太阳直射,和其他条件。仓库保护材料,使其保持良好状态,直到项目使用。总的来说,与传统建筑相比,这会减少材料的浪费,传统建筑往往将材料存放在室外,没有足够的保护。
减少运输量
传统施工需要多条物流路线将材料和工具运送到现场,通常在不同的日期和时间进行。此外,许多承包商和工人每天都到现场进行工作。另一方面,装配式和模块化施工涉及到一个交付点,并且向现场交付数量有限。这些模块在异地组装,然后在有限的时间内送到安装它们的站点。由于这一运送系统,到项目现场的运送数量必然减少。此外,由于模块在交付时就已经组装完毕,因此减少了传统上在项目现场使用的劳动时间,减少了承包商和工人的通勤。
同步制造和现场准备
传统的施工进度表通常先要做建筑工地的准备工作,然后是建筑现场的施工。这不一定是异地和模块化建设的情况。模块的制作与建筑工地的准备工作同时进行,从而整体上减少了施工时间,减少了项目能耗。与传统的现场施工相比,工厂能够更好地控制能源使用和排放。此外,由于模块在内部建造,现场所需的工人更少,从而减少了能源输出、噪音干扰和对现场环境和周围社区的空气污染。
这些只是异地和模块化建筑绿色实践的几个方面。总的来说,装配式和模块化建筑可以帮助减轻其固有的环境可持续性做法对环境的破坏。由于这一点,以及许多其他的好处,模块化建设将继续获得牵引作为一种流行的方法,快速,负担得起的,可持续的建设在美国各地。
英文原文
Offsite construction has numerous benefits. Compared to traditional construction, it can bring efficient practices, new technologies, and increased safety to a project. Another benefit to offsite and modular construction is their reduction in construction and demolition. Environmentally sustainable practices are inherent in many modular delivery systems, typically resulting in less waste than traditional construction. Below are a few reasons why offsite and modular construction are greener ways to build.
Reusability and Recycling of Materials
A significant portion of modular construction takes place in an offsite factory. This factory typically houses project materials and other materials regularly used in modules. Where materials are ordered, but are unused for whatever reason (such as the owner changing their mind, a change in specifications, or otherwise), the materials are not wasted or thrown away. Rather, the materials are recycled and reused. The unused materials can be re-inventoried and stored inside the factory’s warehouse for future use on other projects. In turn, material packaging, like wood pallets, plastic and cardboard, is also reduced. Reusability of materials therefore reduces the overall amount of waste generated from the project.
Control of Material Exposure
Since many of the project’s materials are stored in an offsite factory, the materials are not subjected to outdoor conditions during downtime. They are often stored inside of a warehouse, where they are sheltered from rain, snow, heat, direct sun, and other conditions. Warehouses protect the materials so that they remain in good condition until used on the project. Overall, this results in less wasted materials than traditional construction, where materials are often stored outside without adequate protection.
Reduced Site Visits
Traditional construction requires multiple logistical routes for the delivery of materials and tools to the site, typically taking place at different dates and times. Additionally, many contractors and laborers make daily visits to the site to perform work. Offsite and modular construction, on the other hand, involves a single point of delivery and has a limited number of deliveries to the site. The modules are assembled offsite, then sent in a limited duration to the site where they are installed. Because of this delivery system, there is inherently a reduced number of deliveries to the project site. Additionally, since modules are already assembled upon delivery, it results in decreased labor time traditionally employed on the project site and less commuting by contractors and laborers.
Concurrent Fabrication and Site Preparation
Traditional construction schedules typically depict preparation of the building site, followed by construction of the building onsite. This is not necessarily the case with offsite and modular construction. Modules are fabricated concurrently with the preparation of the building site, resulting in an overall reduction in construction time and less energy used on the project. Factories are better positioned to control energy use and emissions as opposed to traditional onsite construction. Furthermore, with modules being constructed inhouse, less workers are needed onsite, thereby reducing energy output, noise disruption, and air pollution to the site’s environment and the surrounding communities.
These are only a few aspects of offsite and modular
construction’s green practices. Overall, offsite and modular construction can help mitigate damage to the environment with their inherent environmentally sustainable practices. Because of this, and many other benefits, modular construction will continue to gain traction as a popular method for quick, affordable, and sustainable construction throughout the United States.